Wisconsin Winter Wheat Disease Update – June 6, 2018
Damon Smith, Extension Field Crops Pathologist, Department of Plant Pathology, University of Wisconsin-Madison
Brian Mueller, Assistant Field Researcher, Department of Plant Pathology, University of Wisconsin-Madison
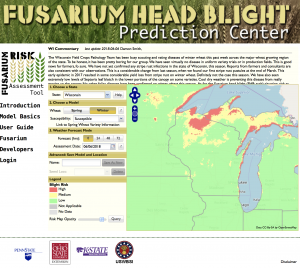
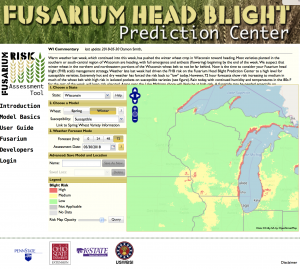
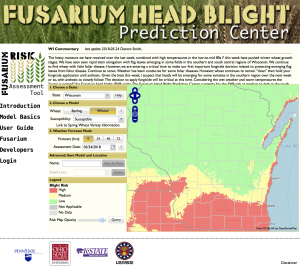
Fusarium Head Blight Risk for June 6, 2018. Visit the Fusarium Head Blight Prediction Center to stay up to date on the latest forecasts.
The Wisconsin Field Crops Pathology Team has been busy scouting and rating diseases of winter wheat this past week across the major wheat growing region of the state. To be honest, it has been pretty boring for our group. We have seen virtually no disease in uniform variety trials or in production fields. This is good news for farmers, for sure.
We have not yet confirmed any stripe rust infections in the state of Wisconsin, this season. Reports from farmers and consultants are also consistent with our observations. This is a considerable change from last season, when we found our first stripe rust pustules at the end of March. This early epidemic in 2017 resulted in some considerable yield loss from stripe rust on winter wheat. Definitely not the case this season. We have also seen extremely low levels of Septoria leaf blotch in the lower portions of the canopy on some varieties. Cool dry weather is preventing this disease from really moving up the canopy. No other foliar diseases have been confirmed on winter wheat this season.
As for the Fusarium head blight (FHB; scab) situation, risk as calculated by the Fusarium Risk Tool, has dissipated over the past week. Two weeks ago, risk of FHB had been estimated to be high on susceptible cultivars. However, cool dry weather has driven the risk to low levels across much of the major wheat production area of Wisconsin. Risk is high still along the Lake Michigan shore and up into Door County. Also elevated and high risk are estimated in Northwest Wisconsin on susceptible cultivars. The situation should be monitored closely in these areas on any crop heading into anthesis. Most of the wheat we have looked at across the southern, south-central, and north-eastern wheat production area of the state is through anthesis or will be by the end of the week. The FHB risk is forecast to be low through this period, in these areas. We will begin scouting for FHB damage in the next week or so, but we anticipate FHB to be mostly low in many areas, with some isolated pockets of higher levels.
It is important to continue scouting over the next couple of weeks. We are transitioning away form making fungicide spray decisions, but it is important to determine the level of FHB present in a particular field, so that proper harvest preparations can be made. We will continue to update you on what we find over the next couple of weeks. However, this is the lowest level of disease on winter wheat I have seen since I have been in Wisconsin. Scout, Scout, Scout!